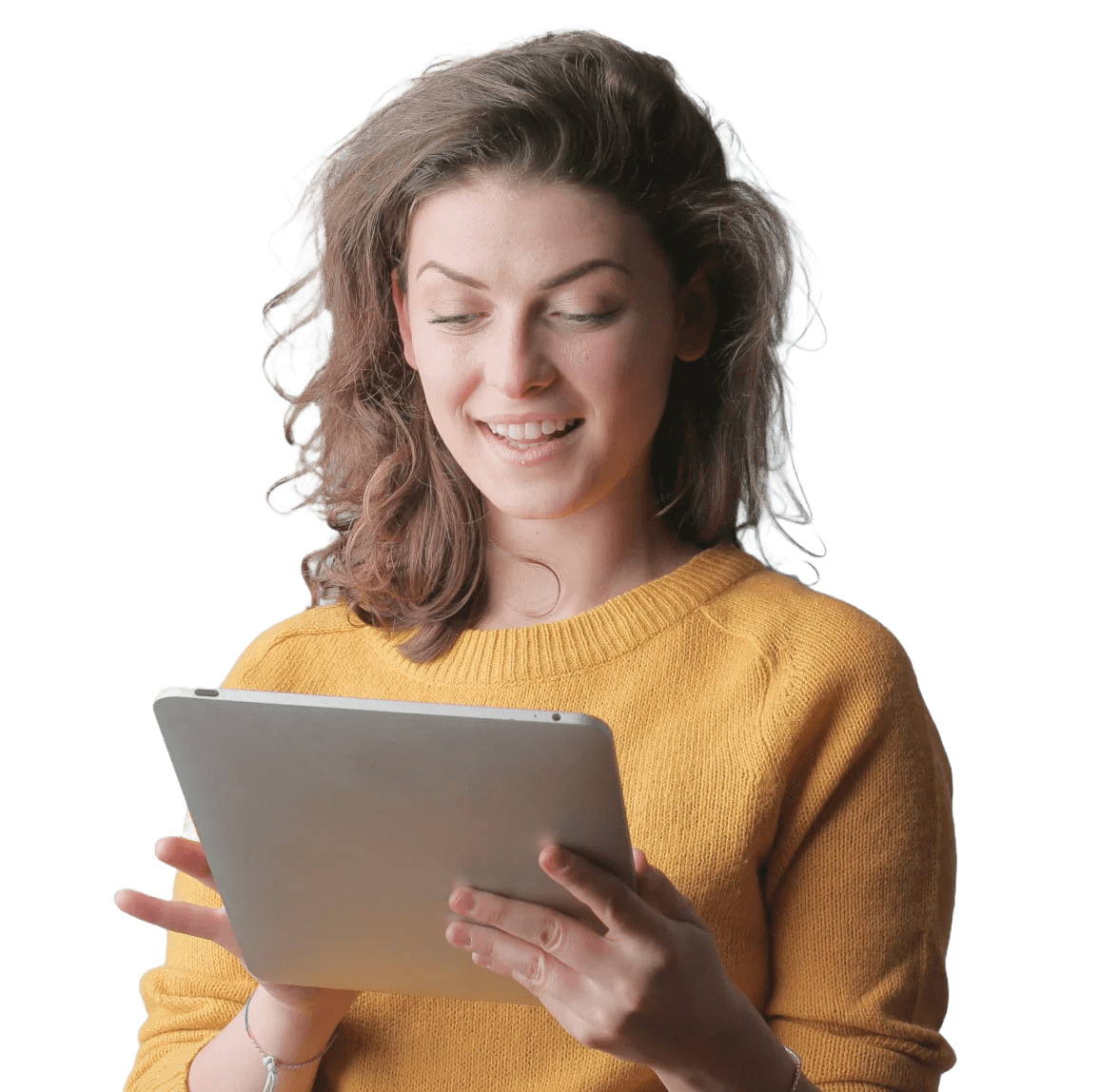
How Trademark Registration Works – Watch Our Expert Process
Wondering how to register a trademark? This short video shows how our experts handle everything—from checking name availability and filing the application to tracking approvals. With fast processing, accurate paperwork, and full legal support, we make trademark registration simple and stress-free.
Have questions? Our trademark specialists are ready to help.
What is Trademark Registration?
Trademark registration is the official process of securing legal protection for your brand under Indian law. It not only helps you safeguard your business or product name (commonly called brand registration) but also protects your logo, tagline, and other visual elements (often referred to as logo registration). This ensures that no one else can use your brand identity without permission, giving you exclusive rights over your intellectual property.
According to the World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO), India has over 2.8 million active trademarks, with nearly 200,000 new applications filed each year. This sharp rise shows that more and more businesses in India are recognizing the importance of protecting their brand identity in today’s competitive and expanding economy.
What Do TM, ®, and © Symbols Mean?
These symbols mean the following:
- ™ (TM): Stands for Trademark. You can use this symbol as soon as you apply for a trademark to indicate that the brand is under protection. It doesn’t require formal registration.
- ® (R): Stands for Registered Trademark. You can use this only after your trademark is officially registered with the Trademark Registry. It signifies legal ownership and exclusive rights.
- © (C): Represents Copyright. This is used to protect original creative works like books, music, artwork, or software—not brand names or logos.
Types of Trademark Registration in India
Trademark registration in India encompasses several categories, each designed to protect different aspects of intellectual property:

Objectives of Trademark Registration
The primary objective of trademark registration, whether you’re focused on overall brand registration or specific logo registration, is to establish exclusive rights over your distinctive brand elements in the marketplace.
- Legal Protection: Obtain exclusive rights to use the mark in connection with specific goods and services.
- Brand Value Creation: Establish and enhance brand equity through legal recognition and protection.
- Consumer Protection: Help consumers identify authentic products and services from trusted sources.
- Infringement Prevention: Gain legal grounds to take action against unauthorized use of similar marks.
- Business Asset Development: Create intellectual property assets that contribute to company valuation.
- Licensing Opportunities: Establish a legal basis for licensing the mark to others for royalty income.
- Territorial Expansion: Secure protection in specific geographical areas and create a basis for international expansion.
- Competitive Advantage: Differentiate products and services from competitors in the marketplace.
Legal Acts and Regulations for Trademark Registration
Trademark registration in India is governed by comprehensive legislation and rules that establish the framework for protecting distinctive marks in commerce.
Characteristics of Trademark Registration
Trademark registration has several distinctive characteristics that define its legal protection and commercial benefits:
1. Exclusive Territorial Rights
Registration grants exclusive rights to use the mark within Indian territory.
- Provides nationwide protection across all states and union territories.
- Creates a legal monopoly over the mark with specified goods/services.
2. Time-Bound Protection
Trademark registration protects for fixed periods with renewal options.
- Initial registration validity is for 10 years from the application date.
- Indefinite protection is possible through successive renewals every 10 years.
3. Use Requirement Flexibility
India’s trademark system accommodates both current and future commercial use.
- Initial registration validity is for 10 years from the application date.
- Indefinite protection is possible through successive renewals every 10 years.
4. Classification-Based Protection
The protection scope is determined by the specified classes of goods and services.
- Registration protects the mark only within the specific classes applied for.
- Multi-class applications are permitted to cover diverse business activities.
5. Public Notice Function
Registration serves as public notification of trademark ownership claims.
- Registered marks appear in the official trademark database.
- The ® symbol can be used to indicate registered status.
6. Transferable Property Rights
Registered trademarks constitute intangible assets that can be transferred.
- Marks can be assigned, licensed, franchised, or used as security for loans.
- These transactions must be recorded with the trademark registry.
7. Infringement Remedies
Registration provides robust legal remedies against unauthorized use.
- Registered trademark owners can seek injunctions, damages, and an account of profits.
- Criminal remedies are available for counterfeiting registered marks.
8. Incontestability Factor
Long-standing registrations gain stronger legal status over time.
- After seven years, registration becomes prima facie evidence of validity.
- This strengthens the mark against certain types of challenges.
Why Should You Register a Trademark?

Securing a trademark for your business, which includes crucial aspects like brand registration (for your name) and logo registration (for your visual identity), offers numerous benefits of trademark registration that enhance brand protection and overall business value:
Eligibility Criteria for Trademark Registration
Eligibility for trademark registration depends on several critical factors. These determine if a mark qualifies for legal protection under Indian trademark law.
- Distinctive Character Requirement — The mark must be capable of distinguishing the goods/services of one undertaking from those of others, avoiding generic or merely descriptive terms.
- Graphic Representation Capability — The mark must be capable of being represented graphically in a clear, precise manner that enables proper examination.
- Legal Use in Commerce — The mark must be used or intended to be used in legal commerce in connection with specified goods or services.
- Non-Deceptive Nature — The mark should not be deceptive or confuse the nature, quality, or geographical origin of the goods/services.
- Non-Prohibited Elements — The mark should not contain prohibited elements like national emblems, flags, or symbols notified under the Emblems and Names Act.
- Legal Entity Status — Applicants must be legal entities (individuals, companies, partnerships, trusts, etc.) capable of owning property.
- Territorial Applicability — For registration in India, the mark must be used or proposed to be used within Indian territory.
- Non-Generic Terminology — The mark cannot consist solely of generic terms that are commonly used in the relevant trade or industry.
Meeting these requirements is essential for successful trademark registration and ensuring your mark receives proper legal protection in the marketplace.
Documents Required for Trademark Registration
Proper documentation is crucial for a smooth trademark registration process, with several key documents required to complete your application:
Choosing the Correct Trademark Class
Selecting the correct trademark class is essential, as it determines the category of goods or services your brand will be legally protected under.
| Trademark Class | Category | Examples |
| Class 1 | Chemicals | Industrial chemicals, adhesives, fertilizers |
| Class 3 | Cosmetics & Cleaning Products | Soaps, perfumes, shampoos, toothpaste |
| Class 5 | Pharmaceuticals | Medicines, health supplements, disinfectants |
| Class 7 | Machinery | Engines, agricultural machines, and machine tools |
| Class 9 | Electronics & Software | Computers, mobile apps, and scientific instruments |
| Class 16 | Paper Goods & Stationery | Notebooks, printed materials, office supplies |
| Class 25 | Clothing & Apparel | Shirts, shoes, jackets, belts |
| Class 30 | Food Products | Coffee, tea, sugar, spices, bakery products |
| Class 35 | Advertising & Business Services | Marketing, consultancy, e-commerce, retail services |
| Class 41 | Education & Entertainment Services | Online courses, coaching, and event management |
| Class 42 | Technology & IT Services | Software development, tech consulting, hosting services |
| Class 43 | Hospitality & Food Services | Hotels, restaurants, and catering services |
How to Register a Trademark in India?
Registering a trademark in India involves several steps governed by the Trade Marks Act, 1999, ensuring legal protection for your brand name, logo, tagline, product packaging, sound mark, or any other distinctive sign. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Fees for Trademark Registration in India
Understanding the financial aspects and potential costs associated with trademark registration is essential for businesses planning to protect their brand identity.
Registration Charges
Trademark registration costs in India involve various official trademark registration fees and professional service charges.
- Official Filing Fees: Rs. 4,500 for individuals/startups/small enterprises and Rs. 9,000 for others per class (online filing).
- Physical Filing Surcharge: Additional Rs. 1,000 if filing physical applications instead of online.
- Expedited Examination Fees: Rs. 20,000 for individuals/startups/small enterprises and Rs. 40,000 for others per class.
- Hearing Attendance Fees: Rs. 1,000- Rs. 5,000 if personal appearances are required during objections.
- Professional Service Fees: Rs. 5,000- Rs. 25,000 for trademark attorneys or consultants handling the registration process.
- Search and Consultation Fees: Rs. 2,000- Rs. 5,000 for comprehensive trademark availability searches.
- Response to Examination Report: Rs. 3,000- Rs. 10,000 for professional assistance with responding to objections.
Additional Compliance Costs
Maintaining trademark rights also involves ongoing compliance costs and potential expenses.
- Renewal Fees: Rs. 9,000 for individuals/startups/small enterprises and Rs. 18,000 for others per class every 10 years.
- Restoration Fees: Rs. 5,000 plus renewal fees if the renewal deadline is missed (within 6 months).
- Assignment Recording: Rs. 9,000 for individuals/startups/small enterprises and Rs. 18,000 for others per mark.
- Change of Name/Address: Rs. 900 for individuals/startups/small enterprises and Rs. 1,800 for others.
- Opposition Defense Costs: Rs. 15,000- Rs. 50,000 for responding to oppositions filed against your application.
- Enforcement Expenses: Legal costs starting from Rs. 50,000 for taking action against infringers.
- Recordal of Licenses: Rs. 6,000 for individuals/startups/small enterprises and Rs. 12,000 for others when licensing the mark.
What Happens After Trademark Registration?
Once your trademark is successfully registered and you receive the certificate, there are important post-registration steps to follow to maintain and enforce your trademark rights.
Step 1: Start Using the ® Symbol
- It signals that your brand is officially protected under Indian law.
- Using the ® symbol helps deter potential infringers.
- Avoid using it before registration, as it may lead to penalties.
Step 2: Monitor for Infringement
Regularly watch the market and trademark journals for possible misuse or similar trademarks.
- Keep an eye out for unauthorized use of your mark.
- Use online tools or legal services to track trademark filings and market use.
- Take prompt legal action if infringement is found, through opposition, cease-and-desist notices, or litigation.
Step 3: Maintain Proper Usage
Consistently use your trademark the way it was registered, to keep your rights active.
- Avoid major changes in spelling, design, or representation without applying for a new trademark.
- Use the trademark in business materials—like packaging, advertising, and invoices.
Step 4: Renew the Trademark Timely
Trademark protection is valid for 10 years and must be renewed to remain in force.
- Apply for renewal before expiry, or within the grace period (6 months after expiry).
- File Form TM-R for renewal with applicable government fees.
- If not renewed, the trademark may be removed from the register.
Step 5: Record Trademark Licensing or Assignment
If you license your brand to someone or transfer ownership, record it officially with the Trademark Registry.
- Submit appropriate forms like TM-P (for licensing) or TM-A/TM-M (for assignments).
- This ensures legal recognition of the licensee or new owner.
Step 6: Enforce Your Rights When Needed
Use legal tools to protect your trademark against infringement or misuse.
- Send legal notices to infringers.
- File for damages or injunction in civil court if required.
- Take part in proceedings like trademark rectification if others misuse or wrongly register a similar mark.
Trademark Registration Certificate
A Trademark Registration Certificate is an official document issued by the government that grants legal protection to your brand name, logo, or slogan. It serves as proof of your exclusive rights to use the trademark in connection with your goods or services.
This certificate helps prevent unauthorized use or infringement by others and strengthens your brand’s identity in the market. Holding a trademark registration certificate also boosts your business credibility and can be a valuable asset for expansion or licensing opportunities.
How to Download a Trademark Registration Certificate?
- Visit the official IP India Trademark Portal: ipindia.gov.in.
- Click on the “Related Links” tab and select “E-Registration Certificate.”
- Enter your Trademark Application Number.
- Verify the details displayed on the screen.
- Click on the “View Certificate” or “Download PDF” option.
- Save the certificate for future use.
How to Check Trademark Application Status?
- Go to the Trademark Application/Registration Status page on ipindiaonline.gov.in
- Enter your Application Number in the provided field
- Click “View” to see the current status (e.g., “Send to Vienna Codification”, “Advertised”, “Registered”, etc.)
- Review any alerts or actions required (such as objection replies or hearings)
- Track updates until you see the status as “Registered”.
Why Choose RegisterKaro for the
Trademark Registration Service?

Here’s why we are the trusted choice for trademark registration services: